EdgeFrame assign_sample¶
-
assign_sample(self, sample_percentages, sample_labels=None, output_column=None, random_seed=None)¶ Randomly group rows into user-defined classes.
Parameters: sample_percentages : list
Entries are non-negative and sum to 1. (See the note below.) If the i‘th entry of the list is p, then then each row receives label i with independent probability p.
sample_labels : list (default=None)
Names to be used for the split classes. Defaults “TR”, “TE”, “VA” when the length of sample_percentages is 3, and defaults to Sample_0, Sample_1, ... otherwise.
output_column : unicode (default=None)
Name of the new column which holds the labels generated by the function.
random_seed : int32 (default=None)
Random seed used to generate the labels. Defaults to 0.
Returns: : _Unit
Randomly assign classes to rows given a vector of percentages. The table receives an additional column that contains a random label. The random label is generated by a probability distribution function. The distribution function is specified by the sample_percentages, a list of floating point values, which add up to 1. The labels are non-negative integers drawn from the range
![[ 0, len(S) - 1]](../../../f_images/math/a714b05c510a3aa90290c5df30b0ac24159a7eb6.png) where
where 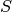 is the sample_percentages.
Optionally, the user can specify a list of strings to be used as the labels.
If the number of labels is 3, the labels will default to “TR”, “TE” and “VA”.
is the sample_percentages.
Optionally, the user can specify a list of strings to be used as the labels.
If the number of labels is 3, the labels will default to “TR”, “TE” and “VA”.Notes
The sample percentages provided by the user are preserved to at least eight decimal places, but beyond this there may be small changes due to floating point imprecision.
In particular:
- The engine validates that the sum of probabilities sums to 1.0 within eight decimal places and returns an error if the sum falls outside of this range.
- The probability of the final class is clamped so that each row receives a valid label with probability one.
Examples
Given a frame accessed via Frame my_frame:
>>> my_frame.inspect() col_nc:str col_wk:str /------------------------/ abc zzz def yyy ghi xxx jkl www mno vvv pqr uuu stu ttt vwx sss yza rrr bcd qqq
To append a new column sample_bin to the frame and assign the value in the new column to “train”, “test”, or “validate”:
>>> my_frame.assign_sample([0.3, 0.3, 0.4], ["train", "test", "validate"]) >>> my_frame.inspect() col_nc:str col_wk:str sample_bin:str /----------------------------------------/ abc zzz validate def yyy test ghi xxx test jkl www test mno vvv train pqr uuu validate stu ttt validate vwx sss train yza rrr validate bcd qqq train
Now, the frame accessed by the Frame, my_frame, has a new column named “sample_bin” and each row contains one of the values “train”, “test”, or “validate”. Values in the other columns are unaffected.